Fun with Domain Controllers Part 1 – Using the set spn command after a Double-Take failback.
From Microsoft:
In Active Directory, the servicePrincipalName (SPN) attribute is a multivalued, nonlinked attribute that is built from the DNS host name. The SPN is used in the process of mutual authentication between the client and the server hosting a particular service. The client finds a computer account based on the SPN of the service to which it is trying to connect.
Setspn.exe: Manipulate Service Principal Names for Accounts
This command-line tool allows you to read, modify, and delete the Service Principal Names (SPN) directory property for an Active Directory service account. SPNs are used to locate a target principal name for running a service. You can use Setspn to view the current SPNs, reset the account’s default SPNs, and add or delete supplemental SPNs.
This post details when you have to use this command following a Double-Take fail back. Last week I was testing Double Take fail over software for virtual systems. In the test senario, we had configured two sites across a WAN link to use seperate domain controllers. Failover worked without a hitch, but when we attempted to fail back the virtual machine (in this case a SQL64 box) on the primary site refused to authenticate on the domain controller of the same site. Double-Take technical support indicated the issue was one of replication, and since the sites were separated by a few thousand miles, that replication might take some time. I had already been on the job for over 12 hours and was ready to go home, so this is what I did to speed up the process:
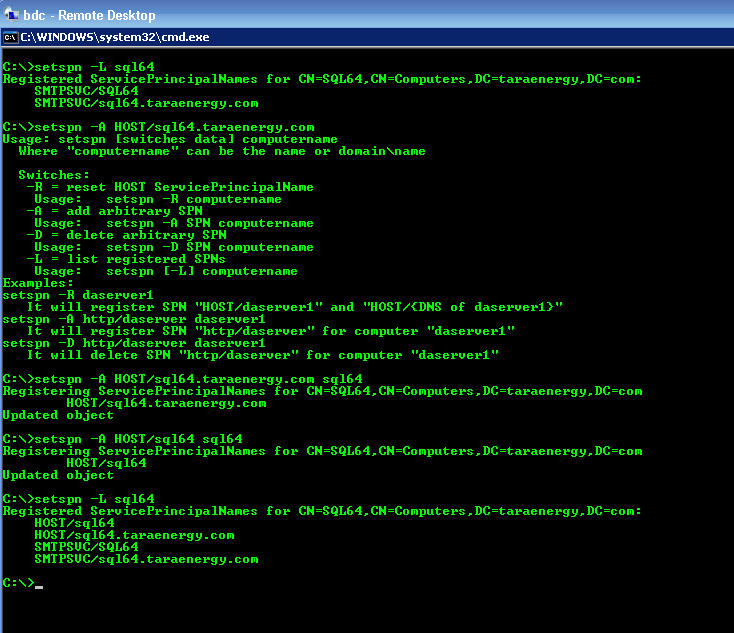
Screen Shot from Remote Desktop Console



